The primary categories of risk at McMaster University are Information and Technology related. Information risk relates to the principles of confidentiality and integrity of information and the systems that support them. Technology risk relates to the principle of availability of technology and its ability to provide information and services when required. Technology risk is directly linked to Disaster Recovery Planning and Business Continuity Planning activities.
To ensure that Information security risk is mitigated, McMaster University must provide appropriate security controls to protect information in a manner that limits unauthorized or accidental disclosure, access, modification or destruction thus exposing the University to an increased potential damage and inability to achieve its strategies and objectives. Similarly, to ensure that Technology risk is mitigated, McMaster University must ensure that it updates and maintains systems and networks and it is leveraging advancements in technology thus impacting the ability to achieve the University’s strategic priorities and objectives.
Risk Management Framework
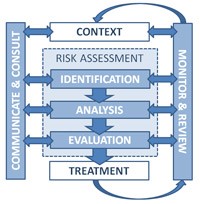
Risk management is better understood via the Enterprise Risk Management framework, which describes the process as follows:
1.Determine the context of the risk management activity
2.Assess the risk through the identification of threats, the analysis of the likelihood and impact, and the evaluation of existing controls and determination of mitigating strategies
3.Approve and implement adequate controls to treat or mitigate the risks identified
4.Monitor the implemented controls to ascertain if risk is reduced to an expected level
5.Communicate the effectiveness of the mitigating strategies in reducing risk to the appropriate oversight individuals or committee
Principles of Information Technology Security
Information security is governed by 3 basic principles known as confidentiality, integrity and availability and together they are called the CIA Triad. These principles must be applied at every step of the security process and must be continuously measured to ensure risk mitigation is at acceptable levels.
CONFIDENTIALITY – Information is disclosed to only those who have the right to know
INTEGRITY – Information is protected against unauthorized or accidental modification
AVAILABILITY – Information is available and usable when required by authorized individuals
